CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
What is La Niña?
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 23, Oct 2021

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration(NOAA) recently declared that La Niña has re-developed.
- Consecutive La Ninas following a transition through ENSO neutral conditions are not uncommon and can be referred to as a “Double-Dip.”
Background:
El Nino and La Nina are part of the El Nino Southern Oscillation(ENSO) cycle.
- In 2020, La Nina developed during the month of August and then dissipated in April 2021 as ENSO-neutral conditions returned.
- For the upcoming winter season, which extends from December 2021 through February 2022, there is an 87% chance of La Nina.
What are the Niño and La Niña?
They are two natural climate phenomena occurring across the tropical Pacific Ocean and influence the weather conditions all over the world.
- While the El Niño period is characterised by warming or increased sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, a La Niña event causes the water in the eastern Pacific Ocean to be colder than usual.
- Together, they are called ENSO or El Niño-Southern Oscillation.
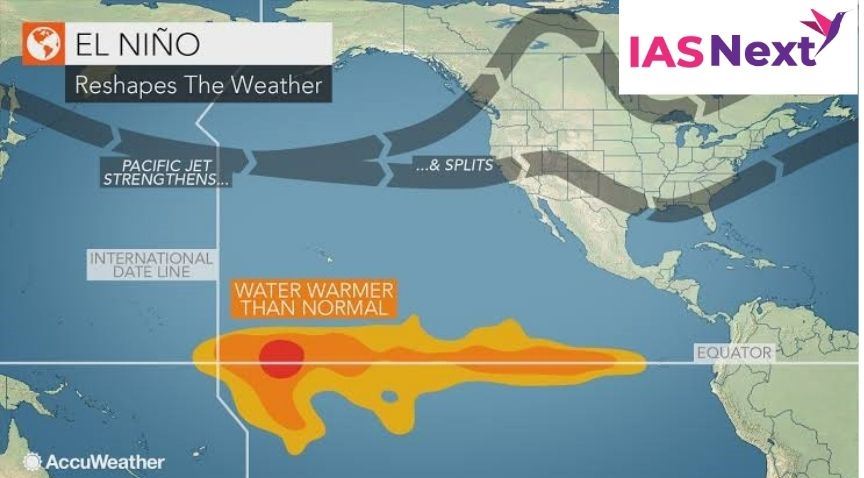
What causes El Nino?
- El Nino sets in when there is an anomaly in the pattern.
- The westward-blowing trade winds weaken along the Equator and due to changes in air pressure, the surface water moves eastwards to the coast of northern South America.
- The central and eastern Pacific regions warm up for over six months and result in an El Nino condition.
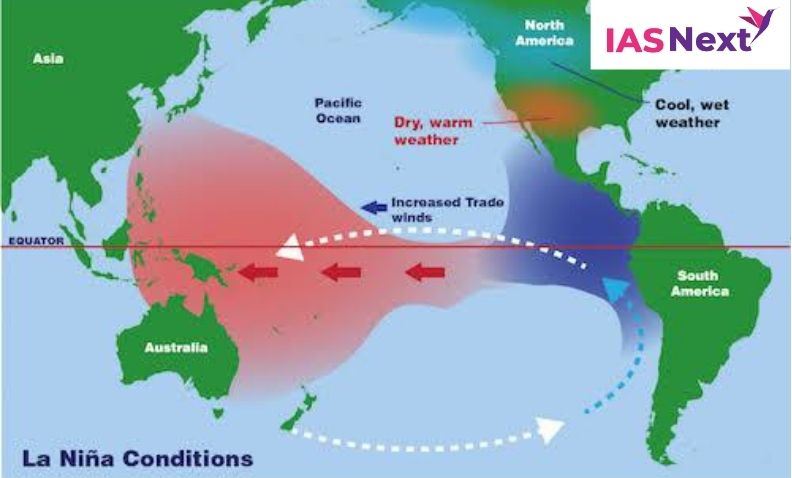
Weather changes because of La Nina:
- The Horn of Africa and central Asia will see below average rainfall due to La Niña.
- East Africa is forecast to see drier-than-usual conditions, which together with the existing impacts of the desert locust invasion, may add to regional food insecurity.
- It could also lead to increased rainfall in southern Africa.
- It could also affect the South West Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclone season, reducing the intensity.
- Southeast Asia, some Pacific Islands and the northern region of South America are expected to receive above-average rainfall.
- In India, La Niña means the country will receive more rainfall than normal, leading to floods.