CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Tonga Volcanic Eruption
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 19, Jan 2022

Context:
Recently, a volcano erupted in the southern Pacific Island of Tonga, which triggered Tsunami waves around the Pacific.
- It is an Undersea Volcanic Eruption consisting of two small uninhabited islands, Hunga-Ha’apai and Hunga-Tonga.
The Tonga Islands occur along the Ring of Fire—a perimeter of heightened volcanic and seismic activity that encircles the Pacific Ocean basin.

The Ring of Fire is a Pacific region home to over 450 volcanoes, including three of the world’s four most active volcanoes – Mount St. Helens in the USA, Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines. It is also sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt.
- Around 90% of the world’s earthquakes occur in the Ring of Fire, and 80% of the world’s largest earthquakes.
Location:
- It stretches along the Pacific Ocean coastlines, where the Pacific Plate grinds against other, smaller tectonic plates that form the Earth’s crust – such as the Philippine Sea plate and the Cocos and Nazca Plates that line the edge of the Pacific Ocean.
- The 40,000 kilometre horse-shoe-shaped ring loops from New Zealand to Chile, passing through the coasts of Asia and the Americas on the way.
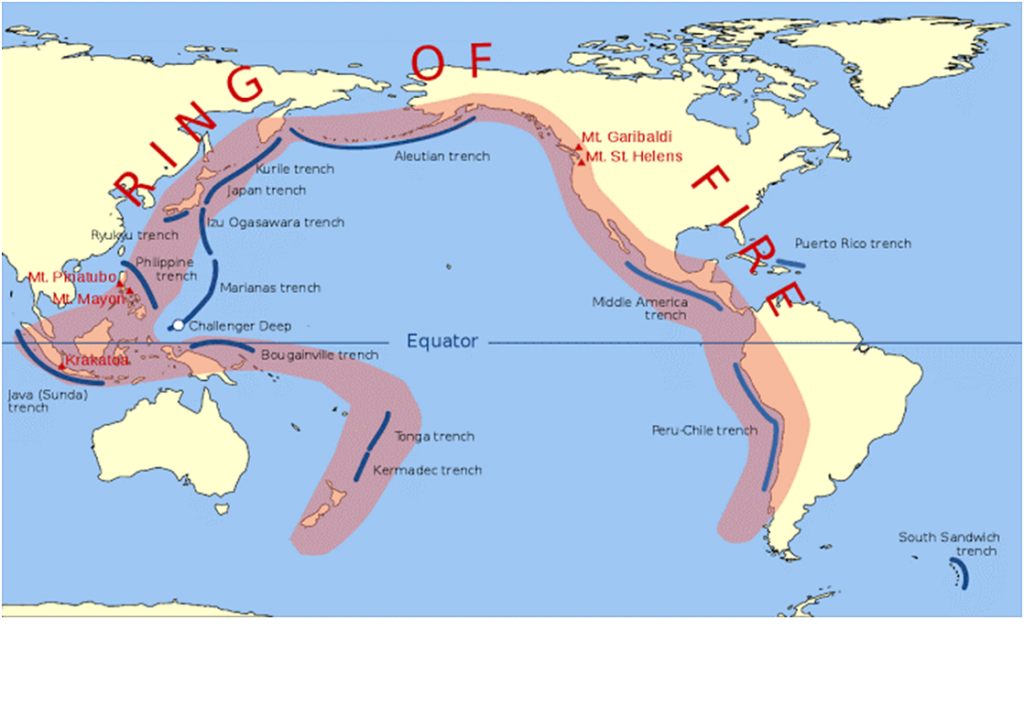
The people most at risk from activity in the Ring of Fire are in the US west coast, Chile, Japan and island nations including the Solomon Islands. These areas are most at risk because they lie on so-called subduction zones – which are boundaries that mark the collision between two of the planet’s tectonic plates.
How was the Ring of Fire formed?
The Ring of Fire is the result from subduction of oceanic tectonic plates beneath lighter continental plates. The area where these tectonic plates meet is called a subduction zone.
Why does the Ring of Fire trigger earthquakes?
- The world’s deepest earthquakes happen in subduction zone areas as tectonic plates scrape against each other – and the Ring of Fire has the world’s biggest concentration of subduction zones.
- As energy is released from the earth’s molten core, it forces tectonic plates to move and they crash up against each other, causing friction. The friction causes a build-up of energy and when this energy is finally released it causes an earthquake. If this happens at sea it can cause devastating tsunamis.
- Tectonic plates usually only move on average a few centimetres each year, but when an earthquake strikes, they speed up massively and can move at several metres per second.