CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Modi launches missions for better cities
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 04, Oct 2021
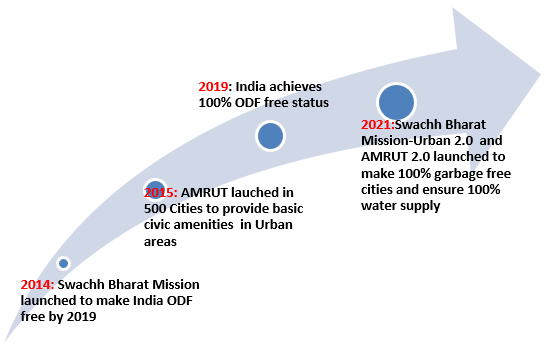
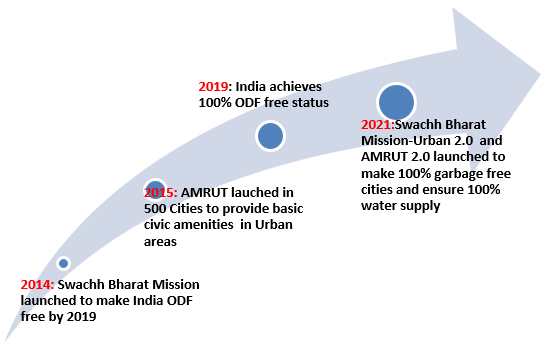
The government has launched the 2nd phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban and Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) to make cities free of garbage, ensuring safe water, and not allow any untreated water discharge into any of the rivers in the country.
Achievement till now:
- 100% Open Defecation Free (ODF)
- 70% of wastes in Indian Cities are being processed (from 20% back in 2014): India is processing about one lakh tonne of waste every day.
- Behavioral Changes: Cleanliness has become a great campaign. PM cited that Children no longer throw Toffee wrappers around but keep them in the pocket to be disposed of in the dustbin later
- National Respect and Pride: The successes of the two missions have given citizens respect, dignity, pride in collective ambition, and unmatched love for the motherland.
- Enhanced finances: Allocation of the fund to the Urban Development Ministry increased from 25 lakh Crore (2007-2014) to 4 lakh Crore (2014-2021).
Key Points of the Mission:
Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U)
- To make all cities 100% ‘garbage free’ from current 70%
- Ensure grey and black water management in all cities other than those covered under AMRUT
- Make all urban local bodies as ODF+ and those with a population of less than 1 lakh as ODF++
- Focus on source segregation of solid waste by utilizing the principles of 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle)
- Scientific processing of all types of municipal solid waste and remediation of legacy dumpsites for effective solid waste management
AMRUT 2.0
- 100% coverage of water supply to all households in around 4,700 urban local bodies by providing about 68 crore tap connections
- 100% coverage of sewerage and septage in 500 AMRUT cities by providing around 64 crore sewers/ septage connections
- Adopt the principles of Circular Economy (Generating wealth from waste using 3Rs)
- Promote conservation and rejuvenation of surface and groundwater bodies
- Data led governance in water management
- Technology Sub-Mission to leverage latest global technologies and skills
- ‘Pey Jal Survekshan’: To promote competition among cities
Renunciation of Indian citizenship now simpler
Reference News:
New guidelines introduced by Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) to simplify the process of renunciation of citizenship for Indians who wish to do so.
- Some of the simplified provisions in the new guidelines include- Uploading of documents online and completion of the process of renunciation within 60 days
- The new form also has a provision mandating the Indian citizen to indicate the reason for renouncing the citizenship
- The uploaded documents have to be submitted to the District Magistrate in case of citizen living in India or an Indian Mission abroad. The applicant will be interviewed before issuing the final certificate
- Also, the guidelines specify that as per the Citizenship act, 1955- “every minor child of that person shall thereupon ceases to be a citizen of India”.
- Concern with the guidelines: The guidelines are not clear if minors would also lose citizenship if only one of the parents gives up her/his Indian citizenship.
- How can citizenship be acquired in India?
Figure: Provisions related to acquiring citizenship
- The citizenship act, 1955 prescribes three ways of losing citizenship:
- By renunciation:
- Any citizen of India of full age and capacity can make a declaration renouncing Indian citizenship
- Such declaration may not be accepted during war.
- Even the minor children of the person who renounces citizenship stands to lose their Indian citizenship. However, when their children attain the age of eighteen, he may resume Indian citizenship
- By termination:
- If a citizen of India voluntarily acquires the citizenship of another country, then he loses the citizenship of India
- However, this provision does not apply during times of war
- By deprivation: Compulsory termination of Indian citizenship by the Central government, in the following conditions:
- Obtained the citizenship by fraud
- Citizen has shown disloyalty to the Constitution of India
- Citizen has unlawfully traded or communicated during the times of war
- Within 5 years of naturalization, the said citizen is imprisoned for a term of two years
- Citizen has been ordinarily resident out of India for a period of 7 years