CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
G-SAP: Securities acquisition plan for market boost
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 12, Oct 2021

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is halting its bond buying under the G-Sec Acquisition Programme(GSAP) for now.
- It said that the measure had succeeded in ensuring adequate liquidity and stabilising financial markets.
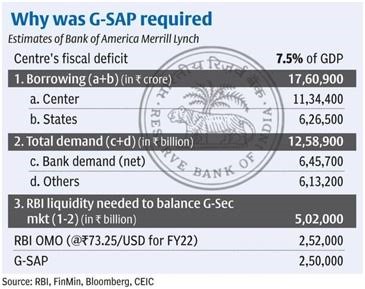
Impacts and outcomes:
Coupled with other liquidity measures, it facilitated congenial and orderly financing conditions and a conducive environment for the recovery.
About the Government Security Acquisition Programme (G-SAP):
The G-Sec Acquisition Programme(GSAP) is basically an unconditional and a structured Open Market Operation (OMO), of a much larger scale and size.
- RBI has called the G-SAP as an OMO with a ‘distinct character’.
- The word ‘unconditional’ here connotes that RBI has committed upfront that it will buy G-Secs irrespective of the market sentiment.
Objective:
To achieve a stable and orderly evolution of the yield curve along with management of liquidity in the economy.
Significance:
- The GSAP would provide more comfort to the bond market. As the borrowing of the Government increased this year, RBI has to ensure there is no disruption in the Indian market.
- The programme will help to reduce the spread between repo rate and the ten-year government bond yield.
- The G-SAP will almost serve the purpose of an OMO calendar, which had been on the bond market’s wish list for a long time.
What is OMO?
Open market operations is the sale and purchase of government securities and treasury bills by RBI or the central bank of the country.
The objective of OMO is to regulate the money supply in the economy.
- It is one of the quantitative monetary policy tools.
How is it done?
RBI carries out the OMO through commercial banks and does not directly deal with the public.
OMOs vs liquidity:
- When the central bank wants to infuse liquidity into the monetary system, it will buy government securities in the open market. This way it provides commercial banks with liquidity.
- In contrast, when it sells securities, it curbs liquidity. Thus, the central bank indirectly controls the money supply and influences short-term interest rates.
RBI employs two kinds of OMOs:
Outright Purchase (PEMO) – this is permanent and involves the outright selling or buying of government securities.
Repurchase Agreement (REPO) – this is short-term and are subject to repurchase.